When shopping for a security camera system, customers typically don't give encoding much thought, but it is crucial to know how surveillance cameras and systems record, store, and playback video. Security cameras greatly benefit from improvements in video encoding as new technology is developed. H.265 or HEVC is the latest innovation in video encoding, and it has some pros and some cons. H.264 is the older encoding technology that has been around since 2003, but that doesn’t mean it’s obsolete yet.
What is H.265?
H.265 (also called HEVC, or "High Efficiency Video Codec") is a technology for compressing video that was developed in the early 2010s by the ISO/IEC Moving Picture Experts Group and the ITU-T Video Coding Experts Group (VCEG) and became a widely accepted standard for encoding in 2016. Most standards for video coding are made with the goal of making encoding as efficient as possible. When compared to H.264, H.265 can reduce the file size of a video by up to 50% while retaining the same quality. But it's important to note that even though H.265 makes files smaller, encoding and decoding them for playback takes more processing power.
How does H.265 work?
The efficiency increase is achieved by a different encoding strategy. The older H.264 technology encodes videos in blocks of up to 16x16 pixels called "macroblocks." With H.264, those blocks are the same size throughout the video. H.265 is able to encode areas of video in various block sizes, from as small as 4x4 pixels up to 64x64 pixels, called “coding tree units." This means H.265 has the ability to encode video blocks that are four times larger. And because the video blocks can be different sizes, H.265 has better motion compensation and improved prediction technology. These improvements combine to allow for lower bitrates, and bitrates are what control how large video file sizes are and how much network bandwidth is required to send and receive a video stream.

Let's recap: H.265 provides lower bitrates for encoding, which allow for:
- Lower bandwidth for video streaming means you can stream more cameras in a 10 Mbps bandwidth stream.
- Smaller file size, which means you can record more video in the same hard drive compared to recording encoded in H.264.
Storage Savings With H.265
The improved encoding strategy that H.265 uses means it requires a lower bitrate than H.264. The ability to lower the bitrate can result in storage savings of up to 50%! In the past, if a surveillance system user wanted to optimize storage space, they had to lower the resolution and frame-rate of their cameras to set a lower bitrate. When the resolution and frame rate are lowered, the image quality is much worse, and the video is not as smooth. When the encoding settings are set to H.265, a user can expect to see the same amount of detail with half the bitrate.
For example, a 4K security camera in H.264 mode will record at approximately 8 Mbps, while in H.265 mode it can record the same quality at 4 Mbps. It’s important to note, however, that it's “up to” 50% savings, and a bitrate of 6 Mbps for H.265 4K is recommended to avoid introducing video artifacting. Video artifacting is caused by video glitches that can occur during the encoding process. Setting a bitrate that is too low for a given resolution and frame-rate will cause video artifacting, regardless if it is H.264 or H.265.
You can run more comparisons of storage savings that can be had with a variety of encoding settings on your security camera systems by using our Security NVR and DVR storage calculator. It lets you compare total bandwidth and storage needed with H.265 and H.264 encoding. You can select different camera resolutions, frames per second, and encoding methods to determine the bitrate for each and all of your cameras. By specifying the total number of recording time, it will also provide you the total DVR hard drive storage you need.
Video Quality
If you compared two files that are the same exact video, one encoded with H.264 and the other encoded with H.265 without any other significant changes in fps and resolution, there wouldn’t really be a noticeable difference in quality. The quality differences between the two only really come into play when you are trying to save storage space or stream video over the internet by reducing the bitrate.

Using the bitrate example from above and applying it to our security cameras, a 4K video stream that is 60 seconds long and encoded with H.264 will be approximately 491Mb in size (8192 Kbps x 60 seconds). The same 4K video encoded with H.265 will be approximately 246Mb (4096 Kbps x 60 seconds), which demonstrates the possible 50% savings. But, as mentioned in the example, using H.265 at 4 Mbps will cause a drop in quality and introduce video glitches. Using the suggested 6 Mbps for 4K H.265 encoding, the file size will be around 368 Mb (6144 x 60 seconds).
Keep in mind that these file sizes are in megabits with a little b (Mb), not megabytes with a big B (MB). For the megabyte values, you can divide the megabit number by 8 to get the megabyte amount.
The important takeaway here is that there is no significant difference in video quality between H.264 and H.265. The video quality actually depends on the bitrate of the video. Setting a bitrate that is too low for either encoding technology will lower quality and cause video artifacts to appear. While H.265 allows for much lower bitrates, H.264 can record high-quality 4K video, just with bigger file sizes.
Advantages of H.265 over H.264
We already talked about the two most important technical benefits of H.265 video encoding technology, which are saving space and bandwidth. You might be wondering how all of the technical details affect the real-world usage of our security camera systems. Below, we’ll explain some reasons why you might want to consider switching your camera's encoding settings to H.265:
Longer Recording Times
We’ve covered this a few times in this article, but it’s the main attraction for using H.265. An up-to-50 percent storage savings when it comes to security cameras is huge! A lot of camera systems record continuously, 24 hours a day. Over time, a 50% savings in storage space will be massive.
Let’s say a system is able to record for 7 days before overwriting old footage using H.264. If that same system had cameras set to H.265 encoding, you could expect it to record for up to 14 days! Unfortunately, as previously stated, savings are not always a full 50%, but it is reasonable to expect at least a 25% savings going from 7 days to 10 or so. How much you save depends on how low you can set the bitrate on each channel before you start to notice a loss in quality.
Lower Internet Speed and Data Requirements
The other benefit of low bitrates is that the video streams can be sent over slower internet connections. Most apps use the lower-resolution substream by default to save data and work around slow internet speeds. The lower bitrate for H.265 means that users can switch to the high-resolution mainstream without using as much data and on slower connections. For more information on how bitrate affects remote viewing, check out our guide on watching security cameras with a slow internet connection.
More WiFi Cameras
Since H.265 requires less bandwidth for data transmission, it also means that WiFi cameras don’t require as much throughput to transmit video wirelessly. This results in the ability to connect more WiFi cameras to an access point or wireless router. In the past, we recommended only connecting a maximum of four WiFi security cameras to a single access point using H.264. You can connect 6 to 8 WiFi cameras to an access point by setting the encoding to H.265 on the cameras.
Disadvantages of H.265
So it seems like H.265 should always be used, right? Sadly, the answer is no. H.265 does have a lot of advantages, but it also comes with disadvantages that can make it more of a burden than a benefit.
Requires a lot of Processing Power
The increased efficiency of H.265 doesn’t come without a cost. The amount of processing power needed to encode and decode video is that cost. This overhead of processing power puts a strain on security camera recorders and means that users cannot expect to set all of their channels to H.265 without slowing their DVR or NVR down. Because decoding H.265 video requires significant processing power, a PC with a powerful CPU, such as one with 4 or 6 cores, will be required to playback one camera at a time.
Playback Compatibility Issues
Another common issue with H.265 is playback compatibility with computers and some smartphones. H.265 is not as universal as H.264, so a third-party plugin called a codec may be required on some devices. While free media player software like VLC and the K-Lite codec exists to make it easier to playback various media files, they do not always include support for H.265 on all computers. In 2018, due to licensing costs, Microsoft started charging 99 cents for H.265 support on Windows computers. Fortunately, most iPhones and Androids include support for playing back H.265 videos for free.
Camera and Recorder Compatibility
Even though a majority of modern IP cameras and DVRs or NVRs support H.265 encoding, not all of them do. This is especially true when mixing brands, vendors, or manufacturers. In order for H.265 to work, both the camera and recorder need to have the ability to encode and decode H.265 video. If you’re interested in taking advantage of H.265 technology, make sure you read the specifications of the cameras and recorders to confirm they support it. Our testing has shown that H.265 encoding over ONVIF connections doesn't always work well when mixing cameras and NVRs from different manufacturers.
What is H.265+/H.264+?
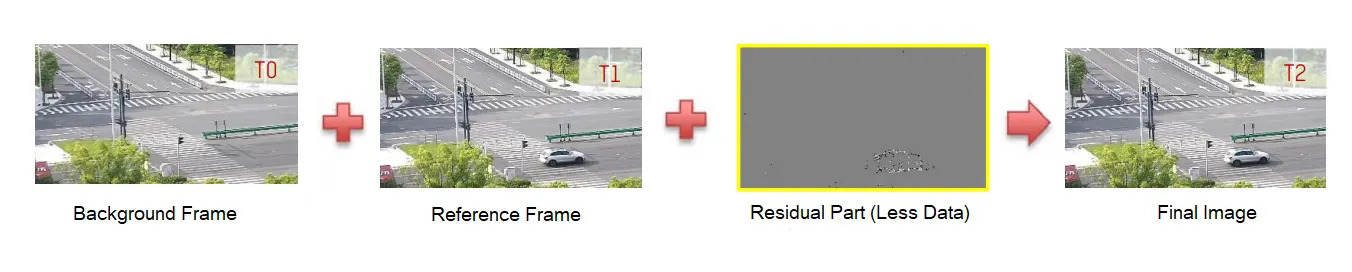
H.265+ and H.264+ are proprietary encoding technology improvements made by manufacturers of surveillance video equipment. These improvements are sometimes called "smart codecs." These smart codec technologies save more space and bandwidth than plain H.265 or H.264 by predictively adjusting the bitrate on the fly based on background and foreground analysis of the scene being recorded. To take advantage of either H.264+ or H.265+ smart codecs, using PoE cameras and NVRs from the same manufacturer is a requirement, as they are proprietary technologies.
Smart codecs provide bandwidth savings by analyzing the scene being captured. If the scene is mostly stable or static, it is used as a background frame or picture. When there are moving objects or interruptions to the stable scene, they are focused and captured in new reference frames. If the object keeps moving, only data from the moving object is added.